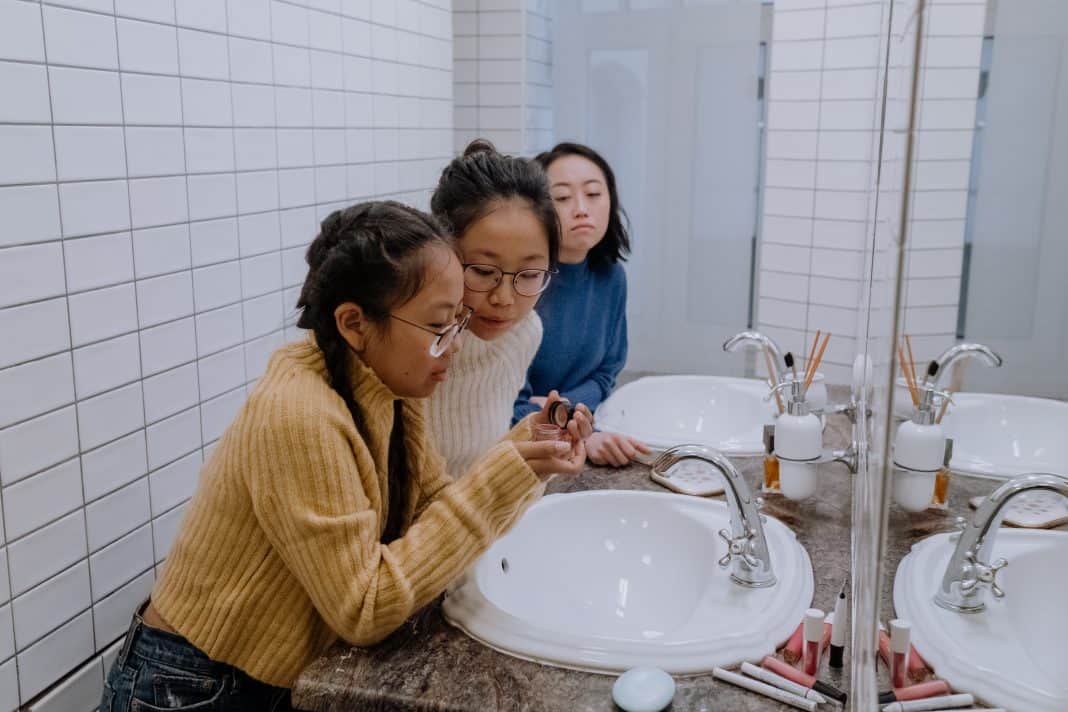
Playing dress-up isn’t an uncommon activity for children of all ages, but at what point does playing pretend—and, specifically, applying and wearing makeup—become too adult of a pastime for kids who are still developing both physically and emotionally? For some parents, that can be a difficult question to ponder, while for others, a definitive answer about how young is too young for makeup is clear. On the one hand, some will argue that there’s no harm in letting a child wear a little blush around the house or lip gloss to the grocery store. “It’s just for fun,” a parent might say. “It makes my kid happy and doesn’t hurt anyone.” Others, however, contend that espousing cosmetics for kids sends a negative message about self-worth by putting too much emphasis on outer beauty at too early an age. Followers of this school of thought believe makeup equals over-sexualization and that it can have dangerous long-term effects. Over half of 12- to 14-year-olds use mascara, eyeshadow, eyeliner, and eyebrow pencils. And 45 percent of that same group of children use foundation and concealer products.
How young is too young?
A study by marketing intelligence agency Mintel found that 80 percent of 9- to 11-year-olds in the U.S. use some form of beauty and personal care products. More specifically, over half of 12- to 14-year-olds use mascara, eyeshadow, eyeliner, and eyebrow pencils. And 45 percent of that same group of children use foundation and concealer products. These percentages include both boys and girls in those age ranges. And while most parents are less likely to worry about their sons’ relationships with cosmetic products, the study goes on to note that 69 percent of boys in the same age range use products including facial cleansers, cologne, lip moisturizers, and hair styling mousses, gels, and creams. Of course, makeup usage tends to elicit more raised eyebrows than cleansers, lip care, and hair styling products, maybe because it’s associated with altering one’s appearance—or maybe because cosmetic products are more gendered than other personal care products. According to Alan E. Kazdin, Sterling Professor of psychology and professor of child psychiatry at Yale University, there is no magic age at which a child should or should not wear makeup. “Oftentimes in our culture, wearing makeup is used as a way to enhance sex appeal. …I think this is what we fear most as parents about sharing makeup with children.” —Erick Kenneth French, LCSW
Just the other day, I had couple in my office describing a recurrent argument about this that has escalated over time. The mother was allowing her 6-year-old daughter and a friend who was over to put makeup on. When the husband came home from work and saw them, he felt triggered and threatened to leave his wife if she didn’t have his daughter remove the makeup before leaving the house.
Why is makeup so triggering—even for dads?
“In some subcultures in this country, wearing makeup simply means putting yourself together and being presentable as a woman,” says French. “But oftentimes in our culture, wearing makeup is used as a way to enhance sex appeal and perhaps further objectify oneself so as to increase magnetism and power over others. I think this is what we fear most as parents about sharing makeup with children.” However a parent feels, Kazdin says it can be a challenge for them to balance their preferences and ideals with a realistic view of how their child will be received by their peers and whatever community they’re being raised in. Kazdin understands why parents might dig their heels in when it comes to tattoos and piercings, acknowledging that they’re “more enduring in terms of impact,” but says that if a child “wears torn jeans and a punk orange hairdo, a parent should probably yield to that because that style is going to drop off and go away.” He encourages parents not to take a firm yes or no stance when it comes to children wearing makeup, but rather to find a happy medium that allows them to wear a certain amount of makeup in a controlled environment. “We are all looking for the fine line of ‘This age is okay to wear makeup’ and ‘This is the age when it’s not okay,’” says Kazdin. “But the parent has to be thoughtful and realistic about it while holding up their standards and helping their kid navigate the pressures of childhood.”
A “Guerilla Feminist” View on Makeup (and Heels)
Katia Grubisic, a mom of two daughters ages 1 and 3, is acutely aware that a child’s view of themselves and how they fit into the outside world starts an early age. “Gendering is so prevalent and can be so insidious for both girls and boys,” says Grubisic, who is a self-described “guerrilla feminist” mom. “I’d like my children to grow up with an open field that includes both makeup and fire trucks. As long as society is pitching one relentlessly over the other, I try my best to balance the equation.” At least one in five girls ages 8 to 18 has negative feelings about themselves when they are not wearing makeup.
Taking A More Laid-Back Approach
Mary Sauer, who lives in Missouri, is taking a more laid-back approach to letting her daughters wear makeup. Sauer says she doesn’t remember the first time her daughters, ages 4 and 6, began to play with and wear her cosmetic products. “They typically wear makeup around the house, but I don’t really make a big deal about it if we happen to go out,” says Sauer, whose daughters really only ever ask to wear lip gloss or eyeshadow. “One time, my daughter asked to wear makeup to church, and I did say no to that, mostly because I was worried about judgment—although when we are out in public and they are wearing makeup, no one has ever said anything to me about it.” Sauer lets her two daughters explore their feminine side without restrictions. “My girls have their own nail polish and lip gloss, but they also wear mine occasionally,” she says. “I’m typically involved in the play, mostly because I like my makeup and don’t want it ruined.” “If whatever form of makeup gives you a feeling of being more yourself, then I think it can be a good thing. But really knowing that to be true for one’s self can require a great deal of honesty and introspection.” —Erick Kenneth French, LCSW
Makeup: A threat to self-esteem, or just the boost we need?
Little kids wearing makeup or putting it on mom or dad can be cute, but tweens and teens wearing makeup on the regular can feel like another thing entirely, especially when it involves them emulating (and sometimes even looking like) adults. Are the impacts of makeup usage at this age really as negative as they can appear? The answer is complicated. In a study conducted by The Renfrew Center Foundation, researchers found that at least one in five girls ages 8 to 18 has negative feelings about themselves when they are not wearing makeup. Another study published by Harvard University explored the possibility that makeup can impact female students’ performance in the classroom. The study found that participants who wore makeup outperformed those who did not—researchers dubbed this “the lipstick effect.” That said, it’s important to note that participants were college students, not middle or high schoolers. French says he’s not familiar with these studies but that he is sure some young girls feel better about themselves “because wearing makeup deters any subtle shaming that might come from their culturally conditioned peers.” “If narcissism and the neurosis of glamor and comparison was not such a predominant force in our culture, then it wouldn’t be a thing,” he says. His thoughts on the lipstick effect? “The answer probably isn’t more makeup.” “The answer is healing the pervasive anxiety that we have been conditioned with since childhood, which is driving these neuroses,” French says. “All that said,” he continues, “I think there is also something to be said for caring for yourself and striving to present yourself to the world in a way that accurately represents how you want to be as your true self. If whatever form of makeup gives you a feeling of being more yourself, then I think it can be a good thing. But really knowing that to be true for one’s self can require a great deal of honesty and introspection.” If a child is curious about makeup play, Kazdin encourages parents to let them explore without scrutinizing their desires. Above all, finding a common ground between parent and child when it comes to when and where the child is allowed to wear makeup will cultivate a healthy and productive discussion. Kazdin says the last thing any parent should do is try to shut down the situation without finding a happy medium. “See if there is a way to compromise so the situation fits in with your child’s life,” says Kazdin. “There is probably not a 3-year-old group that’s wearing endless makeup, but there are probably very few 18-year-olds who aren’t wearing even just a little mascara. Parents have to be flexible and more sensitive to their individual child—and not be too rigid or come down harshly on the child for their desires to wear makeup and fit in with society.” Finally, French acknowledges that judgment and comparison can surface for kids and adults alike as families define their values as they relate to makeup, ways of dress, et cetera: “Instilling a family value of non-judgment is always good, but teaching children to pay attention to their feelings so they can be conscious of what they are being is even better.” “I believe the antidote to judgment or preventing the tendency to shame others”—for example, a peer who wears a lot of makeup or other parents whose makeup rules confound us—“is to really strive to stay honest with one’s self and keep one’s eyes fixed on one’s own struggle.” He says that when we pay attention to our feelings and focus on maintaining our own overall wellbeing, we are “less likely to project our shortcomings onto others and instead feel compassion and understanding about whatever we perceive another’s confusion or struggle to be.” Makeup or no makeup, “the key is to be conscious of what you’re striving to be when you dress yourself up,” says French. Sauer thinks that parents shouldn’t worry so much about what others think. “At the end of the day, you know your child best and need to do what feels right to you as a parent,” says Sauer. “I think that if you want your kids to have a healthy relationship with makeup, the first step is modeling the same thing. If you’re really uptight about how you look, that is what they are going to pick up on, not the rules you set for them.”