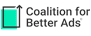I don’t know anyone who doesn’t want a smaller waist and a flatter stomach. Everyone wants nice abs. It’s funny. Even people who already have great abs still want even better ones. I guess that is why there are so many ab machines and gimmicks on the market. I can honestly understand ab machines like the Ab Coaster and the Ab Roller. Those machines actually require a certain amount of work, but can you really get a six-pack by putting a special electronic belt around your waist? You’ve probably seen the infomercials for ab belts claiming to strengthen, tone, and tighten your abs—no exercises required. When I Googled “ab belts,” I couldn’t believe the long list of companies in the business. Just to name a few, there’s the Slendertone, Shred Belt, Abtronic, and the Flex Belt.
How It Works
The ab belt uses electrical muscle stimulation, or EMS, to pass an electrical current through the body, causing your ab muscles to contract. Small electrodes inside the belt come in contact with your bare skin, sending the electrical pulses through your skin to do the work for you. You don’t have to do one crunch or sit up. You just simply slap that belt around your waist and turn up the electrical current until you get the desired level of contraction. When I first heard of ab belts, they reminded me of the TENS unit (transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation device) in physical therapy. But while the ab belt may seem very similar to a TENS unit I’ve used to treat back pain, they have different uses. EMS stimulates muscles to contract, while TENS stimulates nerves. TENS units are typically used to treat chronic and acute pain. EMS is mainly used for muscle retraining and to help prevent muscle atrophy in bedridden patients. How does it feel? Well, I personally think it feels pretty weird. If anyone says it’s relaxing, they either don’t have it up high enough, or they’re lying. Okay, maybe they really aren’t lying and they just like the weird prickly sensation of the electrical current going through their skin. It’s not painful, but I can’t say it’s completely comfortable, either—but neither is doing crunches! How often do you use it? Different brands have different directions, but most recommend wearing the belt for 10 minutes to an hour every day. I’m guessing, like with any exercise, more is better. Just like doing 100 crunches is more effective than doing 10 crunches, using the ab belt for an hour is better than 10 minutes.
Pros and Cons
I did find a study that showed positive results for strengthening muscles with the Slendertone, but the study showed no improvement when it came to actual body composition (body fat, muscle mass, and weight changes), which is what people expect. The biggest con has to do with body fat. Excess body fat may actually prevent the electrical current from getting to the muscle and working properly. Slendertone’s studies were all tested on people with a body mass index under 30, which means they didn’t use it on any obese people in their study. Many of the ab belts claim to burn calories and help you lose body fat, but this claim is just untrue. So, even if the electrical current reaches your muscles through excess body fat and tones your muscle, you will still need to diet and do some cardio if you want to actually see your stronger ab muscles. Lastly, as far as cons go, the Food and Drug Administration has received reports of burns, bruising, and skin irritation from using the ab belts. In addition to some minor injuries, the ab belts can be very harmful to some people. Even quality ab belts can interfere with pacemakers and defibrillators, so most companies will warn people with internal electronic devices not use the ab belt. Ironically, it seems the ab belt could be more beneficial for leaner fitter, people. While it may not decrease body fat or increase muscle size, studies did show an increase in muscle strength and tone. This strength increase would improve resting tone, which means your stomach muscles would do a better job of holding your stomach in nice and flat.
Fit or Flop?
While it could be beneficial for a small population, I personally believe you can get much better results with traditional exercise and diet. Everyone has abs, just like everyone has thigh muscles. You just might not see them under your body fat, and they might need a little firming up. Instead of buying an ab belt, you’d get a lot more for your money if you bought a gym membership. Diet and cardio is the most effective plan of attack against belly fat. Add strength training to tone muscles and reshape the body. Put all three together (diet, cardio and strength training) and you can starts to approach the abs you see on the ab belt advertisements. Because chances are, the models didn’t get that body using the ab belt anyway!